New Arroyo Bahia Conservation Area Protects Essential Water Sources For 80,000 People
May 6, 2022
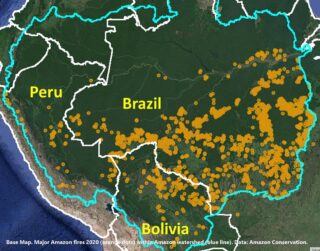
 On May 4, the Arroyo Bahía Conservation Area in the Bolivian Amazon was declared, protecting nearly 10,000 acres of forests and critical water sources for the surrounding local populations. It is the municipality of Cobija’s first protected area. Arroyo Bahía provides valuable ecosystem services in the form of freshwater to 80,000 local people in Bolivia, Peru and Brazil due to the city’s location in the department of Pando, which shares a western border with Peru and a border with Brazil to the north and east. Thus, protecting ecosystems that traverse multiple countries supports the livelihoods of thousands of people.
On May 4, the Arroyo Bahía Conservation Area in the Bolivian Amazon was declared, protecting nearly 10,000 acres of forests and critical water sources for the surrounding local populations. It is the municipality of Cobija’s first protected area. Arroyo Bahía provides valuable ecosystem services in the form of freshwater to 80,000 local people in Bolivia, Peru and Brazil due to the city’s location in the department of Pando, which shares a western border with Peru and a border with Brazil to the north and east. Thus, protecting ecosystems that traverse multiple countries supports the livelihoods of thousands of people.
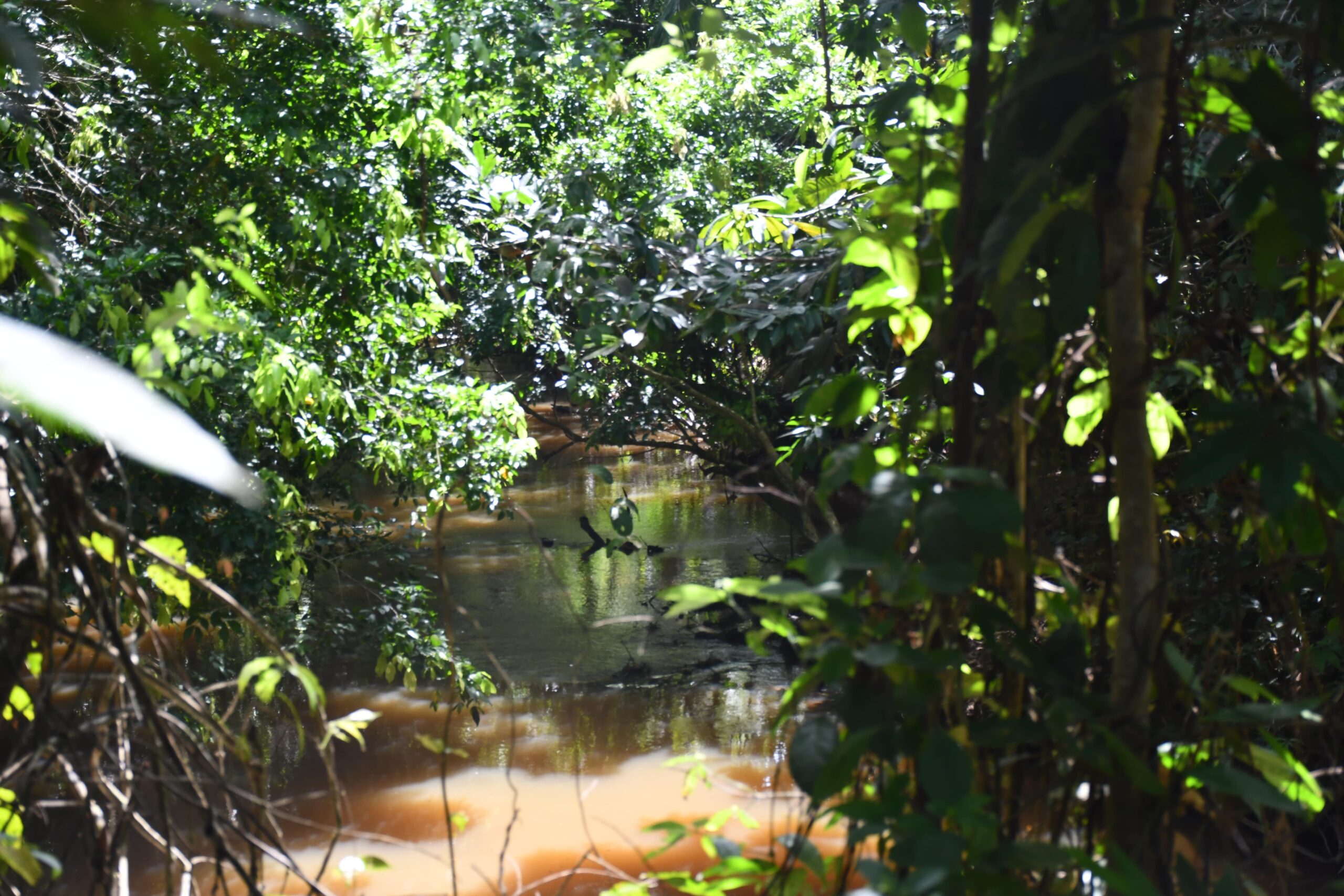
The declaration of this protected area is timely as the upper and middle sections of the Arroyo Bahía basin have been experiencing significant deforestation over the past five years, according to research carried out by Josefina Marín, who serves as the environmental economist of Fundación Natura Bolivia. One of the main reasons for the loss of forest cover has been the increased demand of clearing areas for raising livestock, which causes erosion and soil compaction. This affects the regeneration of forest species and contributes to the sedimentation and clogging of  streams. Consequently, the forest coverage of the banks of the tributary rivers to the stream have been drastically reduced from 1985 to 2008. This, along with the pollution from the dumping of waste, has had terrible consequences for water quality and causes drinkability problems. The Brazil nut harvest has also been reduced lately due to the decrease in the production of the trees and the drop in prices.
streams. Consequently, the forest coverage of the banks of the tributary rivers to the stream have been drastically reduced from 1985 to 2008. This, along with the pollution from the dumping of waste, has had terrible consequences for water quality and causes drinkability problems. The Brazil nut harvest has also been reduced lately due to the decrease in the production of the trees and the drop in prices.
Thus, the establishment of the Arroyo Bahía Conservation Area will protect this basin from contamination and deforestation. It will also support the local peoples’ livelihoods, and mitigate floods and fires. Additionally, the basin is home to great diversity in spite of continuously encroaching human activity. 351 plant species have been identified in two sampling sites, along with 35 amphibian species, 13 reptiles, 185 bird species, 32 mammals, and 30 fish species.
Thank you to support from the Andes Amazon Fund which helped make the declaration of this area possible.

 Loading...
Loading...