MAAP articles #3 and #15 detailed the construction of several new logging roads in the central Peruvian Amazon. Here in MAAP 18, we provide a more comprehensive analysis of the proliferation of logging roads in this section of the Amazon. In Image 18a, we show a high resolution example of a new logging road in this area with active construction during 2015 (see Inset A1 in Image 18c for more context).
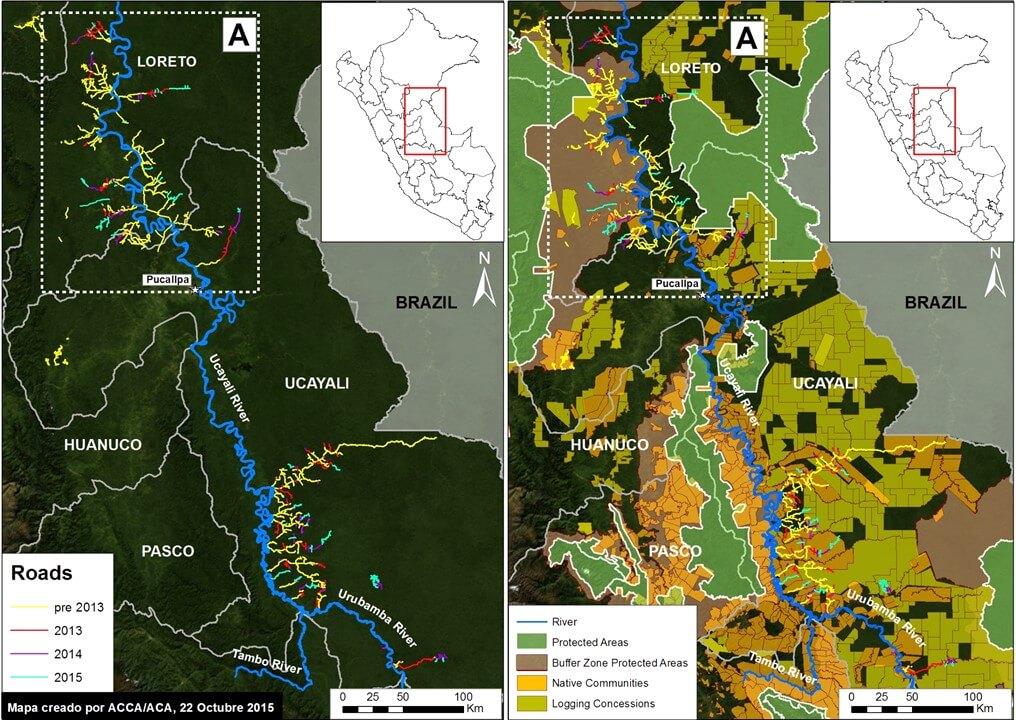
Image 18b illustrates the location of all identified logging roads in the central Peruvian Amazon (southern Loreto and northern Ucayali). Most of these roads are located along the Ucayali River and its headwater tributaries. The left panel highlights just the logging roads, while the right panel also includes protected areas, native communities, and logging concessions.
In Image 18b, we documented the construction of 1,134 km of logging roads between 2013 and 2015 in the central Peruvian Amazon. Of this total, 538 km is in the matrix of logging concessions and native communities in southern Ucayali, 226.1 km is in undesignated areas in southern Loreto, 210 km is in the buffer zone of Cordillera Azul National Park, and 159 km is around the new Sierra del Divisor National Park.
Note that the buffer zone of Cordillera Azul National Park and surroundings of Sierra del Divisor National Park contain logging concessions and native communities, thus the responsibility of forest authority is the regional government.
Determining the legality of these roads is complex. As the right panel highlights, many of these roads are near logging concessions and native communities, whom may have obtained the rights for logging from the relevant forestry authority (in many cases, the regional government).
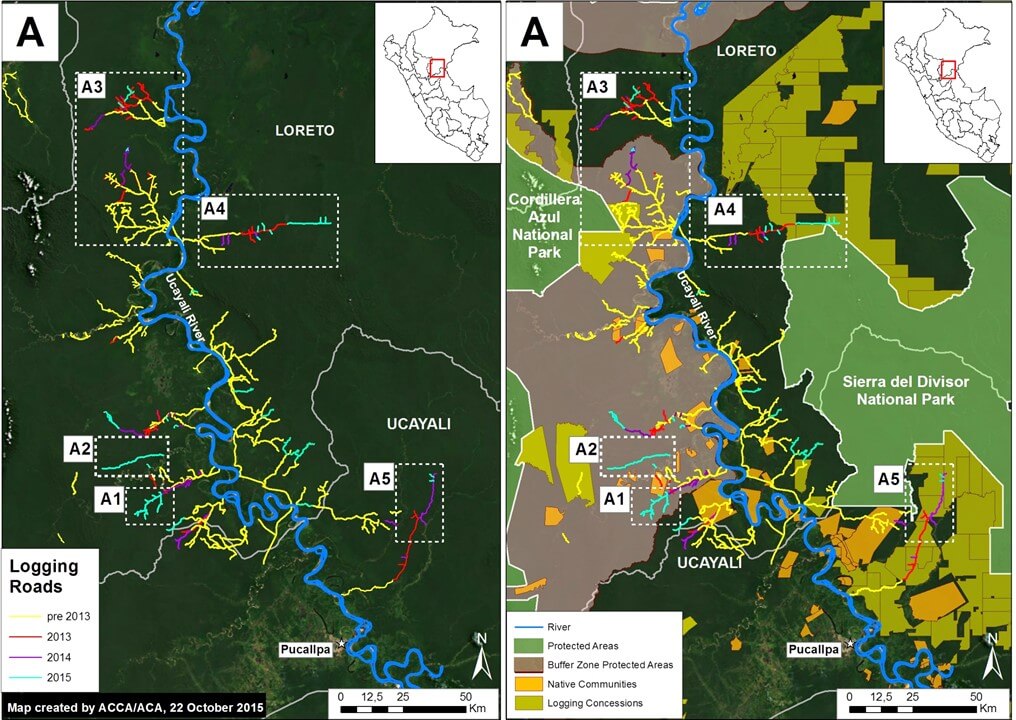
Below, we focus on the logging roads in the northern section of Image 18b (see Inset A).
Zoom A: Logging Roads in Southern Loreto/Northern Ucayali
Image 18c is a zoom of the logging roads shown in the northern section of Image 18a (Inset A), located in southern Loreto and northern Ucayali. It shows five primary areas of interest. Both Insets A1 and A2 correspond to new roads within the southeast buffer zone of the Cordillera Azul National Park with active construction in 2015 (see below for more details).
Insets A3, A4, and A5 correspond to roads with active construction between 2013 and 2015 that have already been featured on MAAP. Inset 3 includes a logging road in the northeast sector of the buffer zone of Cordillera Azul National Park (see MAAP #3 for more details). Insets 3 and 5 show logging roads around the new Sierra del Divisor National Park (see MAAP #15 and MAAP #7 for more details).
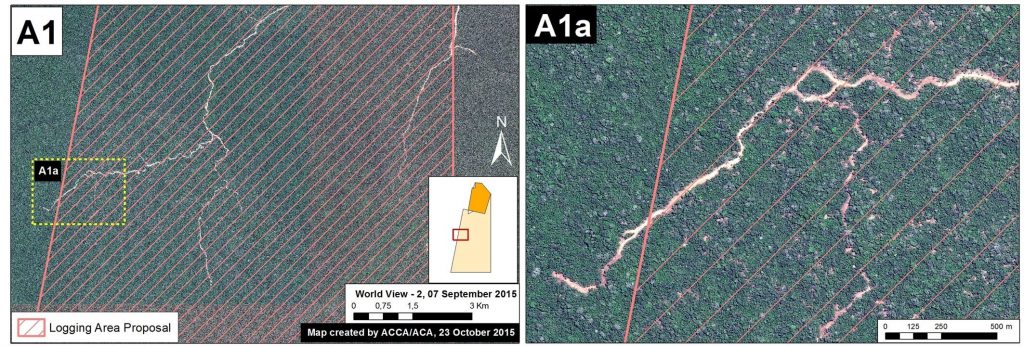
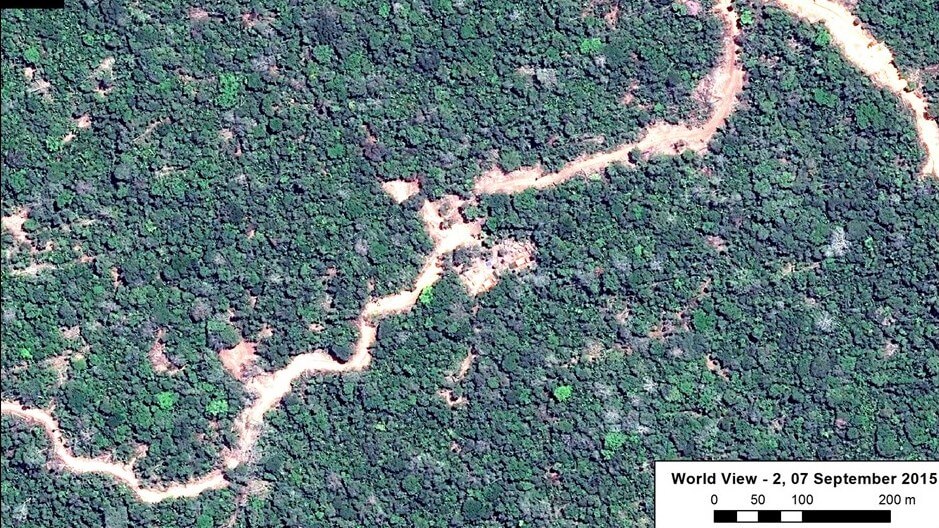
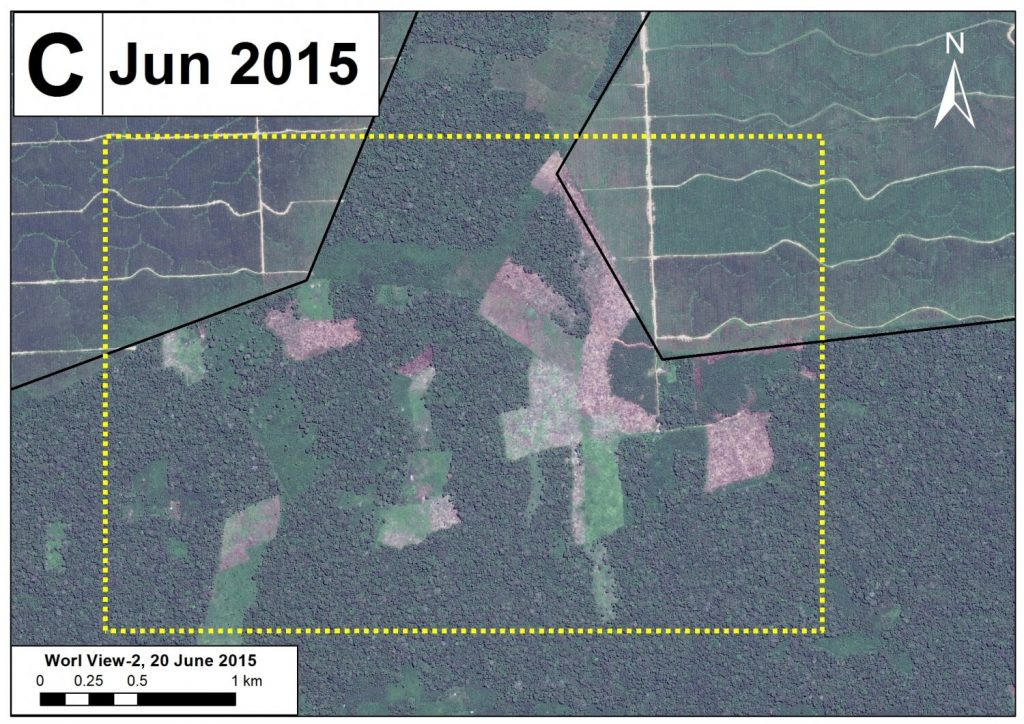
Zoom A1: Logging Roads in Nuevo Irazola
Image 18d provides more details about a new logging road with very recent construction within the southeast buffer zone of Cordillera Azul National Park (See Inset A1 in Image 18C for context). This road has grown 68 km between 2013 and 2015, with more than half of this construction occurring over the past year. According to information obtained from the forestry department within the Regional Government of Ucayali (PRMRFFS), the native community of Nuevo Irazola made a logging permission request for industrial and/or commercial use and prepared an Annual Operating Plan. However, a high-resolution (0.5 m) image shows a recent stretch of the road exceeds the area requested for forestry activities (see Image 18d).
Zoom A2: Rapid Expansion of a Logging Road
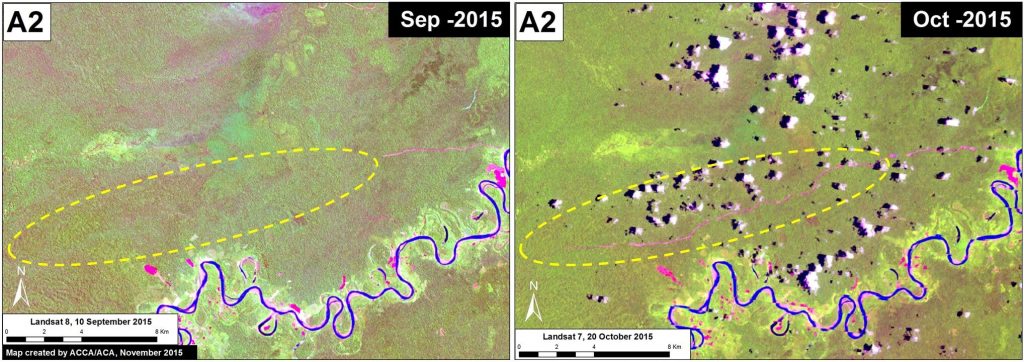
Image 18e illustrates the rapid expansion of another forest road located in the southeast section of the Cordillera Azul National Park buffer zone (See Inset A2 in Image 18C for context). We documented the construction of 29.1 km during the six weeks between September 10 (left panel) and October 20 (right panel), a rate of nearly five kilometers per week. The legality of this road is currently unknown, but note that it is extending in the direction of a forestry concession.
Citation
Novoa S, Fuentes MT, Finer M, Pena N, Julca J (2015) Proliferation of Logging Roads in the Peruvian Amazon. MAAP #18.
Note: MAAP #18 is a collaborative effort between Amazon Conservation Association (ACA), Conservación Amazónica (ACCA), and the Centro de Conservación Investigación y Manejo de Áreas Naturales (CIMA).




 Loading...
Loading...