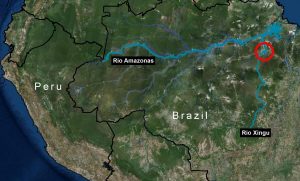
The Belo Monte hydroelectric dam complex, located on the Xingu River in the state of Para in the eastern Brazilian Amazon (see Image 66a), has been controversial since its inception over 15 years ago, due to both environmental and social concerns related to building and operating one of the largest dams in the world in a sensitive environment.
The dam has recently become operational, providing an opportunity to evaluate initial impacts.
The objective of this article is to present satellite imagery, including a time series from 2011 to 2017, that provides insight into major ecological impacts of the hydroelectric dam project.
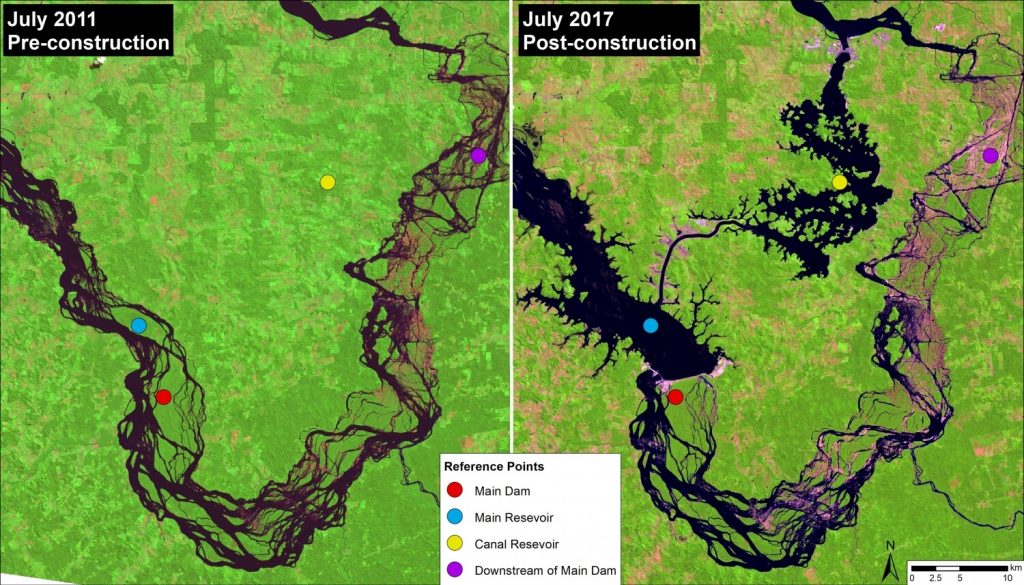
Despite legal challenges and strong opposition from impacted indigenous groups, construction of Belo Monte began in 2011 and the first turbines became operational in early 2017. Image 66b shows a direct comparison of before (left panel, July 2011) and after (right panel, July 2017) dam construction.
The dam is in fact a complex: the main dam (red circle) on the Xingu River creates a main reservoir (blue circle); a canal diverts much (up to 80%) of the river’s flow from the main reservoir to the canal reservoir (yellow circle), which feeds the turbines generating the electricity. As a result, downstream of the main dam is left with a much reduced flow (20%) for a stretch of 100 km. This reduced flow stretch, known as the Xingu River’s “Big Bend,” is home to two indigenous peoples (Arara and Juruna). The reference points in the images show these four areas of the complex across time, including before construction.

 Loading...
Loading...