Celebrate Earth Day like 9-year-old Aya, who was so inspired to protect the Amazon rainforest and all its ecosystem services that her new environmental club’s first fundraiser was held to conserve the Amazon.
 In her third-grade class in Oakland, California, Aya learned about the impact of climate change on the environment and animals. After hearing about the number of species and critical habitats being threatened, Aya knew she wanted to take action. Thus, she started a student-run Stopping Global Warming Club to protect the Earth. They recently held their first fundraiser — a bake sale to protect the Amazon rainforest — that was a huge success, raising $745 that was then matched and tripled to $2,235!
In her third-grade class in Oakland, California, Aya learned about the impact of climate change on the environment and animals. After hearing about the number of species and critical habitats being threatened, Aya knew she wanted to take action. Thus, she started a student-run Stopping Global Warming Club to protect the Earth. They recently held their first fundraiser — a bake sale to protect the Amazon rainforest — that was a huge success, raising $745 that was then matched and tripled to $2,235!
 The inspiration behind Aya’s desire to start the Stopping Global Warming Club arose from her love for animals. “In my opinion, I think a lot of animals are super cute, and hearing about natural disasters and animals dying out made me feel upset,” she recalled. Aya knew she wanted to be a part of a group of like-minded conservationists, but the environmental clubs she researched were geared towards teens or adults. Unfazed, she took matters into her own hands. “When I looked online I saw clubs that are mostly for older people, like 18 or 21 year olds. And so I decided to start a club for younger people.”
The inspiration behind Aya’s desire to start the Stopping Global Warming Club arose from her love for animals. “In my opinion, I think a lot of animals are super cute, and hearing about natural disasters and animals dying out made me feel upset,” she recalled. Aya knew she wanted to be a part of a group of like-minded conservationists, but the environmental clubs she researched were geared towards teens or adults. Unfazed, she took matters into her own hands. “When I looked online I saw clubs that are mostly for older people, like 18 or 21 year olds. And so I decided to start a club for younger people.”
The Stopping Global Warming Club currently has 13 members ranging from 5-13 years old. One is Aya’s friend Mira, who initially joined the club because she wanted to make friends in the neighborhood: “But then I learned a little more about global warming, and then I liked it more than just making friends. I liked helping the environment.” Mira added that her  favorite animal in the Amazon is a capybara, correctly recalling that it is the world’s largest rodent. Now, Mira is even creating a play to stop global warming, telling us excitedly that, “I wrote the script already!”
favorite animal in the Amazon is a capybara, correctly recalling that it is the world’s largest rodent. Now, Mira is even creating a play to stop global warming, telling us excitedly that, “I wrote the script already!”
The group decided to host their first fundraiser in March to support an environmental charity. When a member suggested that it benefit the Amazon rainforest, Aya agreed, as she recognized the major effects that deforestation has on the planet. “Protecting the Amazon rainforest protects those that live there. But also when you cut down a tree, gasses get released which affects people and animals in other places,” she explained. “I chose to support Amazon Conservation because, first of all, it’s not just any organization. It doesn’t just protect the Amazon rainforest, but it also works with indigenous peoples who really know about the forest, who really know about the different animals and plants.” 
The Stopping Global Warming Club’s initial bake sale fundraising goal was $50, which can protect around 100 acres of forest for a year at Amazon Conservation’s Los Amigos Conservation Area. They ended up reaching and surpassing that goal — raising $745 which was then matched and tripled to $2,235. This significant amount can train 20 local members of a firefighting brigade in the Amazon on how to combat and prevent forest fires, which is essential during the annual and destructive fire season that’s already begun.
To others who are inspired to protect the Amazon rainforest, Aya encourages them to do so, saying, “Even if things sound impossible, you should still try to do them and who knows what could happen.” Mira added that, “This is a good cause, and people should start protecting the Amazon.”
This Earth Day, we celebrate young conservationists like Aya and her friends, who have been inspired by the incredible ecosystem services the Amazon offers – like habitat and food for animals and local communities alike. Real change and impactful conservation efforts are critical to the future of the Amazon so that the next generation will also be able to enjoy the many resources the forest provides for years to come. Amazon Conservation is working hard on the ground to ensure a sustainable future for the forest by supporting sustainable livelihoods deep in the Amazon and protecting biodiverse zones in the Andean-Amazon region. With its countless ecosystem services from fresh water, clean air, and climate regulation to health foods, medical treatments and vaccines, and carbon sequestration, the Amazon is truly the greatest forest on Earth.
Thus, we hope that today – on Earth Day – you strive to be like Aya and her friends by taking action to protect the forest and its resources.
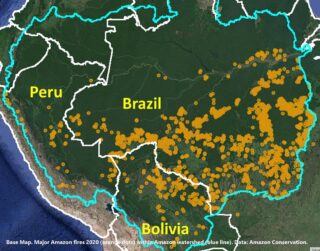
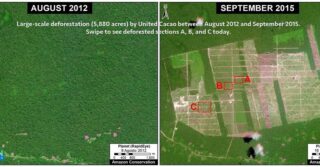
 In 2019, we reported record high levels of gold mining deforestation in the southern Peruvian Amazon, with the Camanti area in the Cusco region representing one of the top three most threatened areas after La Pampa and Upper Malinowski. But this past week the protected area was officially established as the Camanti Sostenible Conservation Concession, which covers 38,172 acres (15,448 hectares).
In 2019, we reported record high levels of gold mining deforestation in the southern Peruvian Amazon, with the Camanti area in the Cusco region representing one of the top three most threatened areas after La Pampa and Upper Malinowski. But this past week the protected area was officially established as the Camanti Sostenible Conservation Concession, which covers 38,172 acres (15,448 hectares).






 Loading...
Loading...